Are you an athlete looking to maximize your performance and recovery? Look no further than the impact of sleep on athletic performance. Sleep plays a crucial role in not only your physical well-being but also in your ability to excel in your chosen sport. By understanding the significance of sleep for athletic performance and recovery, …
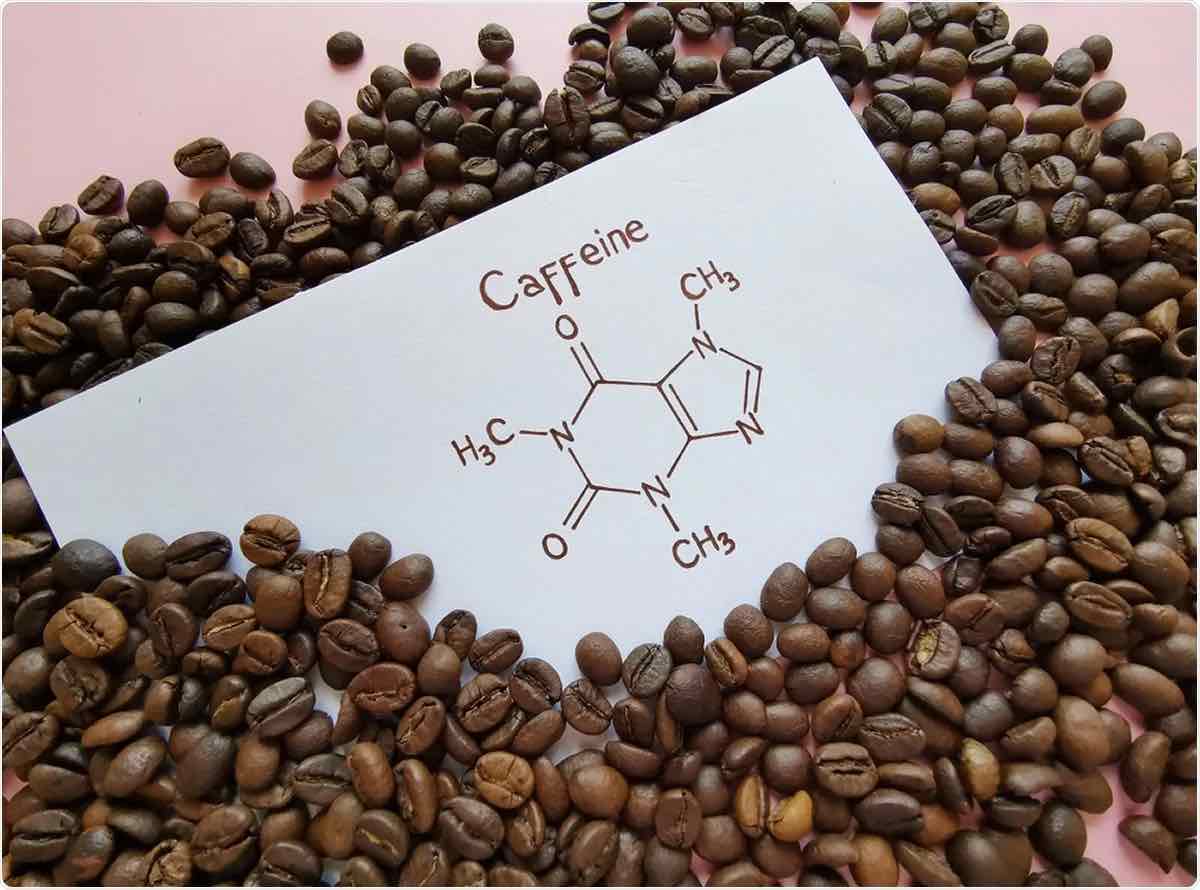
Continue reading “The Impact of Caffeine on Athletic Performance”