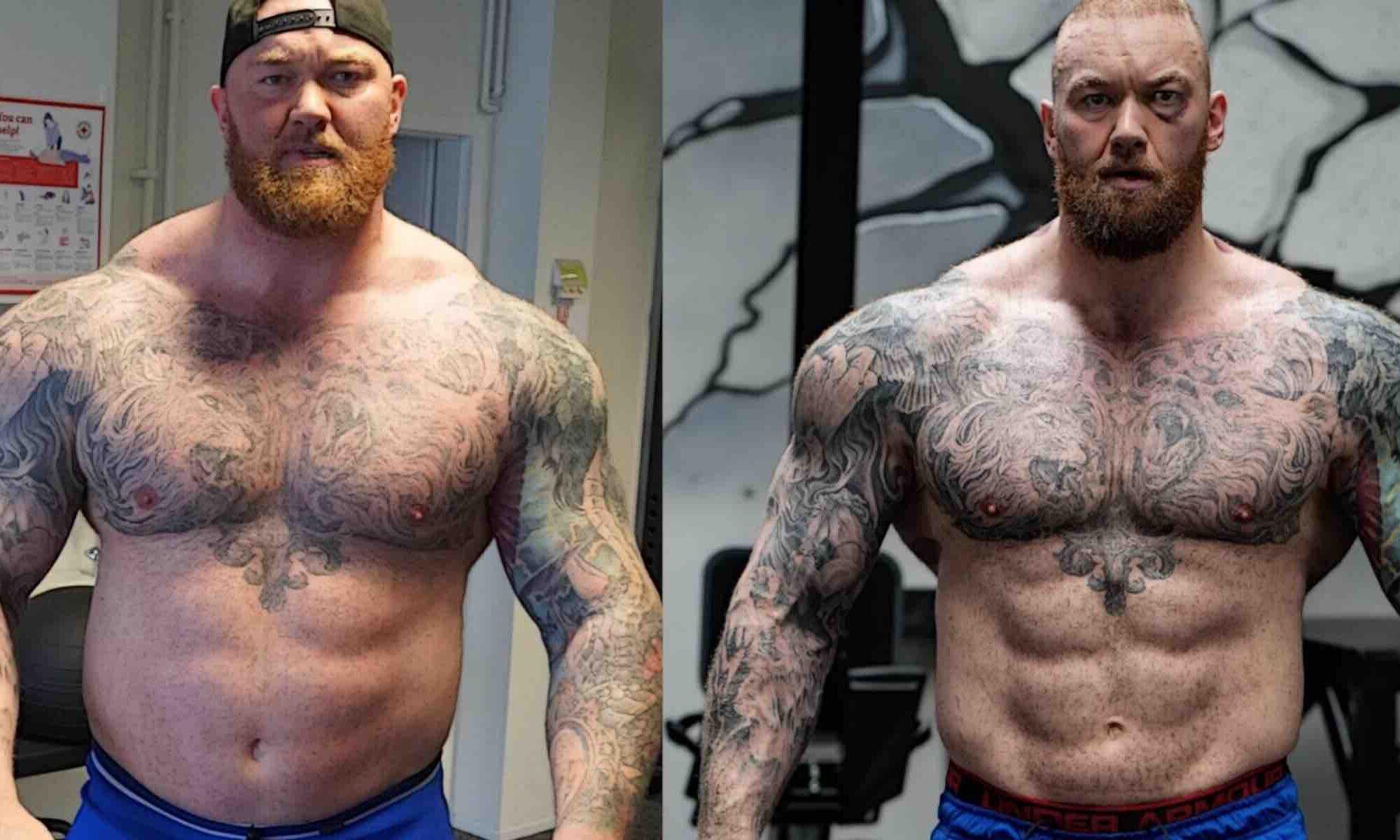
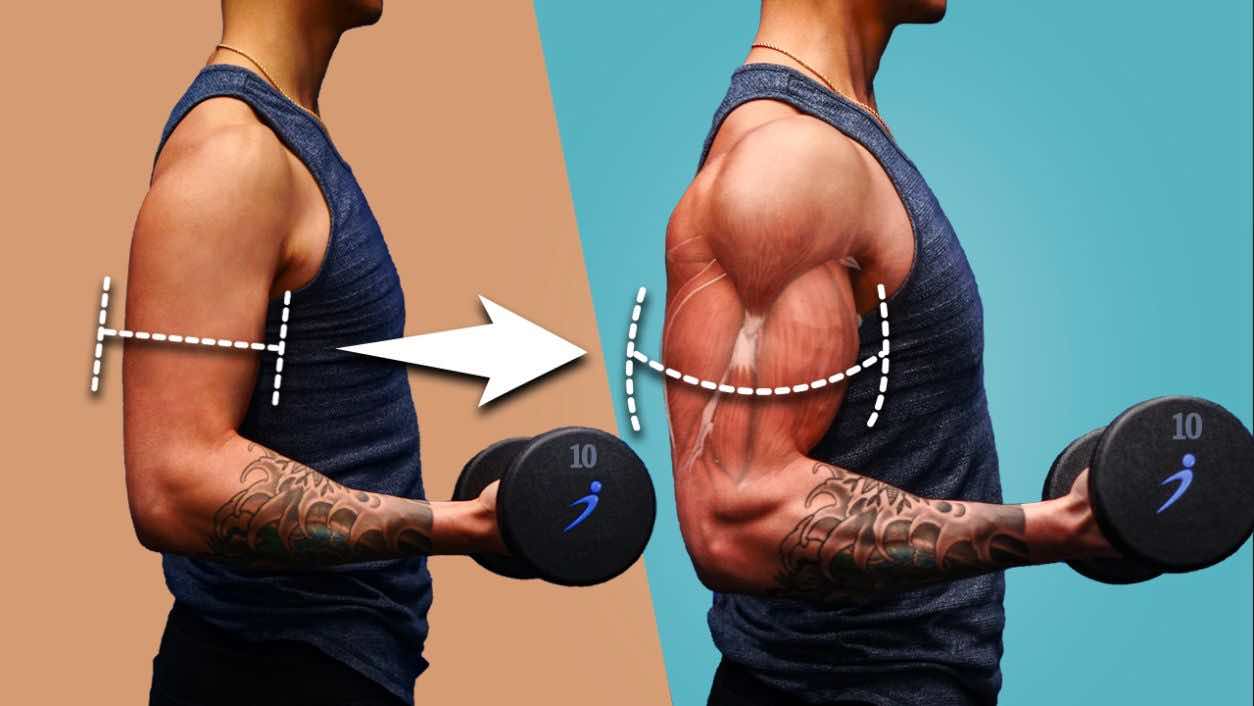
Looking for the best gym trainers near you? Our article has got you covered. Discover the qualities to look for and how to find the perfect trainer to elevate your fitness journey.
3 Benefits of Increasing Your Water Intake
Discover the incredible benefits of increasing your water intake! From improved physical health to enhanced mental well-being, hydration is key. Start prioritizing your hydration today! Continue reading “3 Benefits of Increasing Your Water Intake”
The Unconventional Training Methods of Hafthor Bjornsson (The Mountain)
Hafthor Bjornsson, best known for his portrayal of the character “The Mountain” in HBO’s series “Game of Thrones,” is not just a celebrated actor but also an exceptional strongman. Winning the title of World’s Strongest Man in 2018, Bjornsson showcased the result of years of hard work, determination, and a unique training regime. His unconventional training methods, which have helped him reach the pinnacle of strength sports, are both inspiring and enlightening. Let’s dive into some of these. Continue reading “The Unconventional Training Methods of Hafthor Bjornsson (The Mountain)”
The Key to Muscle Growth
Hey there, Fitness Warriors! Who’s up for unlocking one of the biggest secrets of muscle growth today? We’re talking about Progressive Overload – the key that’s going to unlock the door to your dream physique. So, tighten your laces and get ready, we’re about to embark on a strength journey! Continue reading “The Key to Muscle Growth”
Pushing the Limit: How to Spot Overtraining and Keep It at Bay
Greetings, Warriors of the Wellness Battlefield! We’ve bathed in the pure exhilaration, the intoxicating euphoria that spills forth from conquering a new personal zenith, or prevailing against an arduous, sweat-soaked training session. And yet, the line that separates the noble pursuit of the limits of our physical prowess from a dangerous, self-imposed affliction is thin and elusive. So today, we delve, with earnest hearts and open minds, into an all-too-neglected topic: overtraining. Its manifestations, its root causes, and, crucially, how to steer clear of its insidious grasp. Settle into your favorite chair with a refreshing glass of your beloved post-workout concoction and join us on this enlightening sojourn into the heart of fitness. Continue reading “Pushing the Limit: How to Spot Overtraining and Keep It at Bay”
Exercise and Immunity: How Physical Activity Boosts Your Defenses – Fitness Science Unveiled
We’ve all felt that post-workout rush, the triumph of pushing our bodies, the thrill of feeling alive and invigorated. But, what if I told you there’s even more to love about breaking a sweat? What if your workouts are not just shaping your muscles, but also boosting your body’s natural defenses? That’s right – we’re talking about the fascinating bond between exercise and immunity. Buckle up, because this is going to be an exciting ride!
Continue reading “Exercise and Immunity: How Physical Activity Boosts Your Defenses – Fitness Science Unveiled”
Making the Most of Your Gym Membership: Must-Try Machines and How to Use Them
Maximizing Your Gym Membership: Key Machines and How to Utilize Them Stepping into a gym can sometimes feel like boarding a spacecraft for the first time – a myriad of complex equipment, each with its distinct function. As part of the Fitness Warrior Nation, we understand that harnessing these machines is an integral part of our fitness journey. So, let’s unleash the full potential of your gym membership by identifying the key machines to try and mastering the optimal ways to use them. Continue reading “Making the Most of Your Gym Membership: Must-Try Machines and How to Use Them”
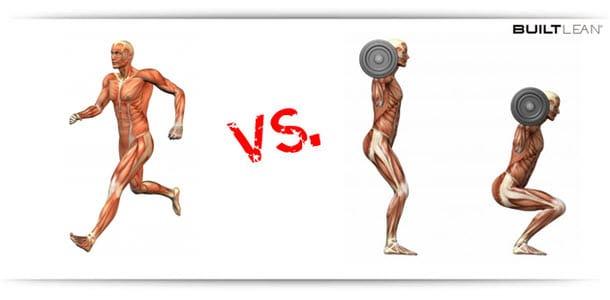
Cardio vs. Weights: The Benefits of Both and How to Balance Them
Are you looking to ignite your fitness routine and achieve optimal results? Look no further than the combination of cardio and weights. In this article, we will explore the benefits of incorporating both forms of exercise into your workout routine and guide you on how to strike the perfect balance between the two. Say goodbye to the endless debate of cardio versus weights, because we’re here to show you that the real magic lies in finding harmony between them. So let’s dive in and discover how you can elevate your fitness journey to new heights!
Cardiovascular Exercise
Cardiovascular exercise, also known as cardio, refers to any form of physical activity that elevates your heart rate and promotes the health of your cardiovascular system. There are various types of cardio exercises, including running, cycling, swimming, dancing, and aerobics. Engaging in regular cardiovascular exercise brings a multitude of benefits for your overall health and well-being.
Benefits for Overall Health
Participating in regular cardiovascular exercise offers numerous benefits for your overall health. It helps to improve lung capacity and oxygen delivery to your muscles, making everyday activities feel less tiring. Cardio also aids in maintaining a healthy weight, reducing the risk of obesity and related health issues such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. Furthermore, cardio exercise strengthens your immune system, leading to fewer instances of illness and faster recovery times.
Improvement in Heart Health
One of the key benefits of cardio exercise is the improvement it brings to your heart health. Engaging in regular cardio workouts strengthens your heart muscle, making it more efficient at pumping blood throughout your body. This efficiency leads to a lower resting heart rate and improved circulation, reducing the risk of heart disease, high blood pressure, and stroke.
Weight Loss and Calorie Burn
If weight loss is one of your goals, cardio exercise can be a valuable tool in your journey. Cardio workouts burn a significant number of calories, helping you create a calorie deficit necessary for weight loss. Whether you choose to go for a run, jump rope, or attend a high-intensity interval training (HIIT) class, the consistent calorie burn during cardio exercises can contribute to shedding excess pounds and achieving a leaner physique.
Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases
Regular participation in cardio exercises has been shown to lower the risk of chronic diseases. Studies have found that engaging in moderate-intensity cardio activities, such as brisk walking or cycling, can help prevent conditions like type 2 diabetes, certain types of cancer, and osteoporosis. Additionally, cardio exercise can improve insulin sensitivity, reduce inflammation in the body, and lower cholesterol levels, all of which contribute to a decreased risk of chronic diseases.
Strength Training
Strength training, also known as resistance training or weightlifting, involves using resistance to build and tone your muscles. This type of exercise focuses on challenging your muscles against an external force, such as dumbbells, resistance bands, or your body weight. Incorporating strength training into your fitness routine brings a range of benefits, from muscle building and toning to increased metabolism and improved bone density.
Muscle Building and Toning
One of the primary benefits of strength training is its ability to build and tone your muscles. When you lift weights or engage in resistance exercises, you create micro-tears in your muscle fibers. As your body repairs these tears, the muscles become stronger and more defined. By consistently challenging your muscles through strength training, you can achieve a lean and toned physique.
Increased Metabolism
Strength training plays a crucial role in boosting your metabolism. Muscles are metabolically active tissue, meaning they burn more calories at rest compared to fat. By increasing your muscle mass through strength training, you can raise your basal metabolic rate (BMR) and burn more calories even when you’re not engaging in physical activity. This increase in metabolism can be particularly beneficial for weight management and achieving a healthy body composition.
Improved Bone Density
Strength training is recognized as an effective way to improve bone density, reducing the risk of osteoporosis and osteoarthritis. As you engage in resistance exercises, your bones adapt to the stress by becoming denser and stronger. This is especially important as you age, as bone loss and decreased bone density become more prominent. Adding strength training to your fitness routine can help maintain and enhance your bone health, promoting overall longevity and quality of life.
Prevention of Injuries
Strength training not only improves your muscle strength and stability but also enhances the integrity of your connective tissues, tendons, and ligaments. This, in turn, can help prevent injuries by providing greater support to your joints and improving their range of motion. A balanced strength training program that targets major muscle groups and focuses on proper form and technique can be highly effective in reducing the risk of injuries, particularly in activities involving repetitive movements or high impact.
Cardio vs. Weights: Debunking the Myths
There are several common myths surrounding the comparison of cardio and weights. Let’s explore and debunk some of these misconceptions:
Myth: Cardio is the only way to lose weight
While cardio exercises can significantly contribute to weight loss by burning calories, it’s important to note that weight loss ultimately depends on creating a calorie deficit. Strength training plays a crucial role in this process, as it helps build muscle mass. Increased muscle mass leads to a higher metabolic rate, allowing your body to burn more calories even at rest.
Myth: Weights make women bulky
One of the biggest misconceptions about strength training, especially among women, is the fear of getting bulky. However, it’s essential to understand that building significant muscle mass requires specific training techniques, nutrition, and often, genetic predisposition. For most women, strength training leads to a lean and toned physique rather than excessive bulkiness.
Myth: Cardio is enough for heart health
Cardiovascular exercise undoubtedly benefits heart health and is an important component of a well-rounded fitness routine. However, incorporating strength training into your regimen can provide additional cardiovascular benefits. Engaging in resistance exercises challenges your heart and can lead to improvements in cardiovascular endurance and overall heart health.
Myth: Weights make you slow and less agile
Strength training can actually enhance your speed and agility. By improving your muscular strength, you can generate more force and power in your movements, enabling you to run faster, jump higher, and react quicker. Additionally, strength training helps to improve your balance and stability, reducing the risk of falls or other accidents.
Myth: Cardio is better for stress relief
While cardio exercises like running or dancing can provide stress relief by releasing endorphins, strength training shouldn’t be ignored in this aspect. Lifting weights and engaging in resistance exercises can offer a sense of empowerment, boost self-confidence, and act as a healthy outlet for stress and anxiety. Plus, the physical benefits gained from strength training can have a positive impact on overall mental well-being.
Finding the Perfect Balance
To find the perfect balance between cardio and strength training, it’s important to consider various factors, such as your goals, body’s needs, scheduling, and listening to your body’s signals.
Determining Your Goals
Start by determining your fitness goals. Are you looking to lose weight, build muscle, improve endurance, or enhance overall fitness? Understanding your goals will help guide your decision-making when it comes to designing your workout routine.
Understanding Your Body’s Needs
Every individual’s body is unique, and it’s essential to understand what your body needs. Consider factors such as your current fitness level, any existing health conditions, and possible limitations or injuries. Consulting with a fitness professional or healthcare provider can provide valuable insights into tailoring your workout routine to suit your individual needs.
Scheduling Your Workout Routine
Finding the right balance between cardio and strength training also involves planning and scheduling your workout routine effectively. Analyze your daily or weekly schedule and consider the time and energy levels you have available for exercise. Aim for consistency by finding a schedule that works for you and incorporating both cardio and strength training sessions.
Incorporating Cardio and Weights
It’s important to incorporate both cardio and strength training into your workout routine to reap the maximum benefits. Depending on your goals, you can choose to alternate between cardio and strength training on different days or combine them within the same session. It’s recommended to aim for a minimum of 150 minutes of moderate-intensity cardio or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity cardio per week, along with at least two days of strength training targeting major muscle groups.
Listening to Your Body
Lastly, listen to your body and pay attention to how you feel during and after your workouts. If you’re experiencing excessive fatigue, soreness, or pain, it may be a sign that you need to adjust your routine or incorporate more rest days. Always prioritize proper form and technique to avoid injuries and make modifications as necessary.

Designing Your Cardio Workout
When designing your cardio workout, consider the following factors to make it effective and enjoyable:
Choosing the Right Cardio Exercises
Select cardio exercises that align with your preferences, goals, and fitness level. Consider activities such as running, cycling, swimming, dancing, or trying out fitness classes. Variety can be key to keeping your cardio workouts fresh and preventing boredom.
Setting Intensity and Duration
The intensity and duration of your cardio workouts will depend on your fitness level and goals. Beginners may start with lower-intensity exercises and gradually increase both intensity and duration over time. High-intensity interval training (HIIT) can be an excellent option for those seeking a time-efficient and challenging cardio workout.
Tips for Effective Cardio Workouts
To make your cardio workouts more effective, set specific goals, such as increasing your distance, improving your pace, or reaching a certain heart rate zone. Incorporate interval training to boost intensity and burn more calories. Monitor your heart rate during cardio sessions using a heart rate monitor or by checking your pulse manually.
Mixing Different Cardio Activities
One way to keep your cardio routine exciting is by mixing different activities. This not only provides variety but also challenges your body in different ways. For example, you can alternate between running, cycling, and swimming throughout the week or even try out new workout classes or sports.
Monitoring Progress and Adjusting
Monitor your progress regularly by tracking your workouts, noting improvements in strength, endurance, or speed, and adjusting your routine accordingly. Gradually increase the intensity or duration of your cardio workouts to continue challenging your body and making progress towards your goals.
Developing Your Strength Training Plan
Consider the following factors when developing your strength training plan for optimal results:
Determining Muscle Groups to Target
Identify the major muscle groups you want to target and include exercises that engage those muscles. Common muscle groups include the chest, back, shoulders, biceps, triceps, legs, and core. Aim to have a well-rounded routine that includes exercises for each of these muscle groups.
Selecting the Appropriate Weights
Choosing the appropriate weights is crucial for an effective strength training workout. Start with lighter weights and gradually increase the resistance as your muscles grow stronger. The weight should be challenging enough to complete the desired number of repetitions with proper form but not so heavy that it compromises your technique.
Structuring Your Strength Workouts
Structure your strength workouts by dividing your routine into different training splits. A common split is the push-pull-legs split, where you focus on pushing exercises (e.g., chest press, shoulder press) on one day, pulling exercises (e.g., rows, pull-ups) on another day, and leg exercises (e.g., squats, lunges) on a separate day. This split allows for optimal muscle recovery and prevents overtraining.
Incorporating Compound and Isolation Exercises
Incorporate a mix of compound and isolation exercises in your strength training routine. Compound exercises, such as squats and deadlifts, engage multiple muscle groups simultaneously, providing functional strength benefits. Isolation exercises, such as bicep curls and tricep extensions, target specific muscles to enhance their definition and symmetry.
Gradually Increasing Weight and Difficulty
To continue making progress in your strength training, it’s important to gradually increase the weight and difficulty of your exercises. As your muscles adapt to the stimulus, you need to provide continued challenge to promote growth and strength gains. Consider incorporating techniques like progressive overload, incorporating supersets, or using resistance bands to continue challenging your muscles.
Benefits of Combining Cardio and Weights
By combining cardio and weights in your fitness routine, you can experience multiple benefits that enhance your overall fitness:
Maximized Calorie Burn
Combining cardio and strength training leads to a higher overall calorie burn during and after your workout. Cardio exercises burn calories during the activity, while strength training increases muscle mass, leading to a higher metabolic rate and more calories burned at rest. This combination can be highly effective for weight management and optimizing your body composition.
Improved Body Composition
The combination of cardio and strength training helps improve your body composition by reducing body fat and increasing muscle mass. While cardio exercises contribute to overall calorie burn and fat loss, strength training promotes muscle growth and improves muscle definition. This results in a toned and lean physique, enhancing your overall appearance.
Enhanced Cardiovascular Endurance
Incorporating both cardio and strength training into your routine can improve your cardiovascular endurance. While cardio exercises primarily target your aerobic capacity and endurance, strength training can enhance your anaerobic endurance by improving your body’s ability to tolerate lactic acid buildup and sustain effort over time. The combined effect leads to enhanced overall cardiovascular endurance, allowing you to perform your daily activities or sports with ease.
Increased Strength and Muscle Tone
Strength training plays a crucial role in developing muscular strength and definition. By targeting specific muscle groups through resistance exercises, you can increase your strength, power, and overall muscle tone. Cardio exercises alone may not provide the same level of strength and muscle-building benefits that strength training can offer.
Balanced Overall Fitness
Combining cardio and strength training in your fitness routine promotes a balanced overall fitness level. Cardiovascular exercise improves your endurance, stamina, and heart health, while strength training enhances your muscular strength, power, and bone density. This combination of cardiovascular and muscular fitness contributes to a well-rounded and functional fitness level.
Sample Workout Routines
Here are a few sample workout routines that incorporate both cardio and strength training:
Alternate Days: Cardio and Strength
- Monday: 30 minutes of running or cycling (moderate intensity)
- Tuesday: Strength training targeting upper body (chest, back, shoulders, biceps, triceps)
- Wednesday: Rest or low-intensity activity (e.g., yoga, stretching)
- Thursday: 30 minutes of swimming or rowing (high intensity)
- Friday: Strength training targeting lower body (legs, glutes)
- Saturday: 30 minutes of HIIT workout or cardio kickboxing
- Sunday: Rest or low-intensity activity (e.g., walking, light stretching)
Circuit Training
Perform a series of strength exercises with minimal rest in between, incorporating cardio bursts between sets or circuits. For example:
- Warm-up: 10 minutes of dynamic stretching or light cardio (e.g., jogging in place)
- Circuit 1: Squats, push-ups, dumbbell rows, jump rope (30 seconds), repeat for 3 sets
- Circuit 2: Deadlifts, shoulder press, lunges, mountain climbers (30 seconds), repeat for 3 sets
- Circuit 3: Bicep curls, tricep dips, planks, high knees (30 seconds), repeat for 3 sets
- Cool-down: 10 minutes of static stretching
Interval Training
Alternate between high-intensity cardio intervals and strength training exercises. For example:
- Warm-up: 10 minutes of light jogging or cycling
- Set 1: Sprint for 30 seconds, followed by 1 minute of bodyweight squats, repeat for 5 sets
- Set 2: Stationary bike sprints for 30 seconds, followed by 1 minute of push-ups, repeat for 5 sets
- Set 3: High knees for 30 seconds, followed by 1 minute of dumbbell lunges, repeat for 5 sets
- Cool-down: 10 minutes of walking or light stretching
Total Body Workouts
Perform exercises that engage multiple muscle groups simultaneously, incorporating cardio intervals in between sets. For example:
- Warm-up: 10 minutes of dynamic stretching or light cardio (e.g., jumping jacks)
- Set 1: Barbell squats, bench press, rowing machine (500 meters), repeat for 3 sets
- Set 2: Deadlifts, shoulder press, elliptical machine (1 minute), repeat for 3 sets
- Set 3: Lunges with dumbbells, lat pulldowns, stationary bike (2 minutes), repeat for 3 sets
- Cool-down: 10 minutes of static stretching
Specialized Training Programs
Depending on your specific goals or interests, you can explore specialized training programs such as CrossFit, boot camps, or sports-specific workouts. These programs often combine cardio and strength training in a structured and challenging way, allowing for comprehensive fitness improvements.
Nutrition and Recovery
Proper nutrition and recovery are vital components of a successful fitness routine. Consider the following factors to support your cardio and strength training efforts:
Fueling for Cardio and Weights
To fuel your workouts, consume a balanced diet that includes carbohydrates, protein, and healthy fats. Carbohydrates provide energy for cardio exercises, while protein supports muscle recovery and growth after strength training. Opt for whole foods such as fruits, vegetables, lean meats, whole grains, and healthy fats like nuts and avocados.
Proper Hydration
Staying hydrated is crucial for maintaining optimal performance during both cardio and strength training. Aim to drink water regularly throughout the day, and hydrate before, during, and after your workouts. Consider electrolyte-rich beverages, especially during intense or prolonged exercise, to replenish essential minerals lost through sweat.
Post-Workout Nutrition
After your workouts, prioritize post-workout nutrition to support recovery and muscle growth. Consume a combination of protein and carbohydrates within 30-60 minutes after your workout. This can be in the form of a protein shake, Greek yogurt with berries, or a balanced meal that includes lean protein and whole grains.
Rest and Sleep Importance
Proper rest and sleep are essential for your body to recover and adapt to the stress of exercise. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to support your overall health, muscle recovery, and hormone balance. Incorporate rest days into your fitness routine to allow your body time to repair and rebuild.
Injury Prevention and Recovery
To prevent injuries, prioritize proper warm-up and cool-down routines before and after your workouts. This includes dynamic stretching, foam rolling, and mobility exercises specific to your body’s needs. If you experience pain or signs of injury, don’t hesitate to seek professional medical advice for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Final Thoughts and Conclusion
Achieving a well-rounded and effective fitness routine requires finding the perfect balance between cardio and strength training. By combining these two types of exercise, you can maximize the benefits for both your physical and mental health. Remember to align your workout routine with your goals, listen to your body’s needs, and continually evaluate and adjust as necessary. With the right balance of cardio and weights, coupled with proper nutrition and recovery, you can experience long-term benefits and enjoy a healthy and active lifestyle.
Continue reading “Cardio vs. Weights: The Benefits of Both and How to Balance Them”
Lactic Acid: Friend or Foe of Your Workout? Unraveling the Mystery
Are you a fitness enthusiast looking to optimize your workout performance? If so, you may have heard conflicting information about lactic acid and its impact on your training. This article aims to unravel the mystery surrounding lactic acid by exploring its role in exercise and its effects on your body. Whether it’s a friendly ally or a formidable enemy, understanding lactic acid’s role can help you make informed decisions to enhance your fitness journey. So let’s dive in and discover the truth about lactic acid!
What is Lactic Acid?
Lactic acid is a compound that is produced in the body during certain metabolic processes, particularly during high-intensity exercise. It is a byproduct of the breakdown of glucose in the absence of oxygen, known as anaerobic metabolism. Lactic acid is produced when the demand for energy in the muscles exceeds the supply of oxygen. This compound plays a crucial role in various physiological processes and has both positive and negative implications for exercise performance and recovery.
Production of Lactic Acid in the Body
The production of lactic acid in the body occurs through a process called glycolysis. In glycolysis, glucose is broken down into pyruvate, which can then be further metabolized to either produce more energy in the presence of oxygen or converted into lactic acid in the absence of oxygen. This process is essential for providing energy to the muscles when oxygen supply is limited, such as during high-intensity exercise or when the body is under stress.
Anaerobic vs Aerobic Metabolism
To understand the relationship between lactic acid and exercise, it is important to distinguish between anaerobic and aerobic metabolism. Aerobic metabolism relies on the presence of oxygen to break down glucose and produce energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). This is the primary energy system used during low to moderate intensity exercise.
On the other hand, during high-intensity exercise or when oxygen supply is limited, anaerobic metabolism takes over. In this process, glucose is rapidly broken down to produce ATP and lactic acid. Anaerobic metabolism allows for a quick and efficient energy production but comes at the cost of lactic acid accumulation in the muscles.
The Relationship between Lactic Acid and Exercise
Lactic Acid as a Byproduct of High-Intensity Exercise
During high-intensity exercise, the demand for energy exceeds the body’s ability to supply oxygen to the muscles. This triggers the reliance on anaerobic metabolism, leading to the production of lactic acid. As the intensity of exercise increases, so does the production of lactic acid. This process results in an accumulation of lactic acid in the muscle tissue.
Correlation between Lactic Acid Build-Up and Muscle Fatigue
There has long been a misconception that lactic acid is the direct cause of muscle fatigue and soreness. However, recent research suggests that lactic acid accumulation is not the primary culprit. Instead, it is the increased acidity in the muscles, resulting from the accumulation of hydrogen ions (H+) during anaerobic metabolism, that contributes to muscle fatigue. While lactic acid does contribute to the increased acidity, it is not solely responsible for muscle fatigue and soreness.
Lactic Acid and Muscle Soreness
Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness (DOMS)
Delayed onset muscle soreness, commonly known as DOMS, refers to the muscular pain and stiffness that develops 24 to 72 hours after exercise. It is particularly common after engaging in activities that the body is not accustomed to or when exercising at high intensities. The exact cause of DOMS is still not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of factors, including microscopic damage to muscle fibers, inflammation, and the production of metabolic byproducts such as lactic acid.
Lactic Acid’s Role in DOMS
Contrary to popular belief, lactic acid does not play a significant role in the development of DOMS. While lactic acid may contribute to the increased acidity in the muscles during exercise, it is not directly responsible for the muscle soreness experienced in the days following intense physical activity. The muscle damage and inflammation caused by the exercise itself are thought to be the primary drivers of DOMS.
Lactic Acid and Performance
Effects of Lactic Acid on Athletic Performance
The accumulation of lactic acid during high-intensity exercise can have both positive and negative effects on athletic performance. On one hand, lactic acid can serve as an additional source of energy for the muscles, allowing them to continue contracting even when oxygen supply is limited. This can enhance performance and help athletes push through fatigue.
On the other hand, excessive lactic acid buildup can lead to a decrease in muscle pH, impairing muscle contraction and causing fatigue. This can negatively impact performance and lead to a decline in athletic output. It is crucial for athletes to find the optimal balance between lactic acid production and clearance to maximize performance.
Strategies to Reduce Lactic Acid Build-Up
To minimize the negative effects of lactic acid buildup, athletes can employ various strategies to enhance lactic acid clearance and reduce its accumulation. One approach is to incorporate high-intensity interval training (HIIT) into their workouts. HIIT combines short bursts of intense exercise with periods of active recovery, allowing the body to better tolerate lactic acid and improve its clearance.
Furthermore, proper hydration, adequate nutrition, and sufficient rest can also support lactic acid clearance and optimize performance. Additionally, athletes can focus on proper breathing techniques during exercise to enhance oxygen delivery and minimize the reliance on anaerobic metabolism.
Lactic Acid and Endurance Training
Adaptations to Lactic Acid during Endurance Training
Endurance training involves prolonged, sustained exercise that challenges the body’s aerobic capacity. Over time, the body undergoes various adaptations to improve its ability to utilize lactic acid as a fuel source, reducing the reliance on anaerobic metabolism. These adaptations include increased mitochondrial density, improved lactate threshold, and enhanced clearance mechanisms for lactic acid.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Lactic Acid in Endurance Activities
The management of lactic acid is of particular importance in endurance activities. When properly trained, athletes can take advantage of lactic acid’s role as an additional energy source and delay the onset of fatigue. However, excessive lactic acid buildup can still hinder performance, leading to a decrease in speed, power, and overall endurance.
It is essential for endurance athletes to find the necessary balance between lactic acid production and clearance to optimize performance and delay the onset of fatigue. This can be achieved through proper training, pacing strategies, and fueling strategies to support both aerobic and anaerobic energy systems.
The Role of Lactic Acid in Recovery
Lactic Acid Clearance and Recovery
After intense exercise, the body begins to clear lactic acid from the muscles to restore normal pH levels and facilitate recovery. Lactic acid clearance occurs primarily through a process called oxidative metabolism, where lactic acid is converted back into pyruvate and further metabolized to produce energy.
Influence of Lactic Acid on Recovery Time
While lactic acid clearance is an important aspect of the recovery process, it is important to note that the presence of lactic acid does not necessarily correlate with longer recovery times. Recovery time depends on various individual factors, including training status, nutrition, sleep, and overall training load. It is important for athletes to prioritize proper recovery strategies to optimize the clearance of lactic acid and restore muscle function.
Myths and Misconceptions about Lactic Acid
Lactic Acid as the Main Cause of Muscle Fatigue
One common misconception is that lactic acid is the primary cause of muscle fatigue during exercise. As discussed earlier, lactic acid itself does not directly lead to muscle fatigue. Instead, it is the accumulation of hydrogen ions and the resulting increase in muscle acidity that contribute to fatigue.
Lactic Acid as a Toxin
Another myth regarding lactic acid is that it is a toxic substance that needs to be eliminated from the body. In reality, lactic acid is a natural byproduct of energy production and plays a vital role in many physiological processes. The body has effective mechanisms in place to remove lactic acid and maintain proper pH balance.
Practical Implications of Lactic Acid Understanding
Optimizing Training Programs
A comprehensive understanding of lactic acid’s role in exercise can help optimize training programs for athletes and fitness enthusiasts. By strategically incorporating high-intensity training, varying intensities, and proper recovery periods, trainers and coaches can help athletes improve their performance and delay the onset of fatigue.
Leveraging Lactic Acid in Exercise
Lactic acid can be leveraged in exercise through interval training, lactate threshold workouts, and other specific training protocols. By progressively challenging the body’s ability to tolerate and utilize lactic acid, athletes can enhance their overall performance and endurance.
Conclusion
Lactic acid is a complex molecule that plays a significant role in exercise and athletic performance. It is a byproduct of anaerobic metabolism and can both enhance and hinder athletic output, depending on its accumulation and clearance. While lactic acid is often misunderstood and associated with muscle fatigue and soreness, it is important to recognize its essential role in energy production and physiological processes. By understanding and properly managing lactic acid levels, athletes can optimize their training, enhance performance, and improve recovery. So, rather than considering lactic acid as a foe, let’s embrace it as a friend that can help us push our limits and achieve our fitness goals.
The Science of Sleep and Recovery for Athletes: Essential Insights and Strategies
In “The Science of Sleep and Recovery for Athletes: Essential Insights and Strategies,” discover the vital role that sleep plays in an athlete’s performance and recovery. This article explores the deep connection between quality sleep and an athlete’s physical and mental well-being. Gain valuable insights into the science behind sleep and how it can optimize athletic performance. Furthermore, uncover effective strategies to ensure athletes get the restorative sleep they need to excel in their respective sports. Whether you’re a professional athlete or a recreational enthusiast, this article will enlighten you on the science-backed approaches to sleep and recovery that can elevate your athletic performance to new heights.
Importance of Sleep for Athletes
Effects of Sleep on Athletic Performance
Sleep plays a crucial role in enhancing athletic performance. When you consistently get enough quality sleep, your reaction time, coordination, and accuracy improve, allowing you to perform at your best. Lack of sleep, on the other hand, can have negative effects on your performance. It can lead to decreased speed, strength, and endurance, making it harder for you to reach your full potential as an athlete.
Benefits of Adequate Sleep for Athletes
Getting enough sleep provides numerous benefits for athletes. Firstly, it promotes muscle recovery and repair, helping to reduce the risk of injuries and improving overall athletic performance. Additionally, sleep enhances memory consolidation, allowing you to better learn and retain new skills and strategies. Furthermore, sufficient sleep improves your immune function, helping to prevent illness and keep you healthy throughout your training and competition periods.
Negative Impact of Sleep Deprivation on Athletes
Sleep deprivation can have detrimental effects on athletes. It impairs cognitive function, negatively impacting decision-making, problem-solving, and concentration abilities. Additionally, inadequate sleep alters hormone levels, leading to increased levels of cortisol, which can hinder muscle recovery and growth. Moreover, sleep deprivation can result in mood disturbances, such as increased levels of irritability, anxiety, and depression, affecting both your athletic performance and overall well-being.
Understanding Sleep Cycles
Stages of Sleep
Sleep is divided into two main stages: non-REM (rapid eye movement) sleep and REM sleep. Non-REM sleep is further divided into three stages: N1, N2, and N3. N1 is a light sleep stage, N2 is a deeper sleep stage where the majority of our sleep occurs, and N3 is the deep sleep stage associated with physical restoration and growth.
REM Sleep and its Significance
REM sleep is characterized by rapid eye movements, vivid dreaming, and increased brain activity. It is crucial for cognitive restoration and emotional regulation. During REM sleep, your brain strengthens neural connections, helping with memory consolidation and learning. It is also believed to play a role in creativity and problem-solving skills.
Non-REM Sleep and its Benefits
Non-REM sleep, specifically the deep sleep stage (N3), is essential for physical restoration and recovery. During this stage, your body repairs damaged tissues, strengthens muscles, and releases growth hormones. Non-REM sleep is critical for athletes as it promotes muscle growth, overall recovery, and increased energy levels for optimal performance.
Optimal Sleep Duration for Athletes
Recommended Sleep Guidelines for Athletes
For athletes, it is generally recommended to aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night. This duration allows for sufficient time to go through multiple sleep cycles, ensuring you obtain enough deep sleep and REM sleep for optimal physical and cognitive recovery. However, individual athletes may have varying sleep needs, and it’s important to listen to your body’s signals and adjust your sleep duration accordingly.
Individual Variations and Sleep Needs
While the recommended sleep duration for athletes falls within the 7-9 hour range, it is essential to recognize that individual variations exist. Factors such as age, training load, and genetic predispositions can influence an athlete’s specific sleep needs. Some individuals may require slightly more or less sleep to feel fully rested and perform at their best. It’s crucial to pay attention to your body’s signals and make adjustments to your sleep routine accordingly.
Factors Influencing Sleep Duration
Several factors can influence the duration of sleep an athlete needs. Training intensity, volume, and frequency can impact an athlete’s sleep needs, with more demanding training regimens often requiring longer sleep durations. Additionally, factors such as stress, travel, and competition schedules can disrupt sleep patterns and impact the quality and quantity of sleep an athlete obtains. It’s important to consider these factors and make appropriate adjustments to ensure adequate sleep is prioritized.
Sleep Quality and Environment
Creating an Ideal Sleep Environment
To optimize sleep quality, it’s important to create an ideal sleep environment. Your sleep environment should be cool, dark, and quiet. Consider investing in blackout curtains or an eye mask to block out any external light sources. Use earplugs or a white noise machine to minimize noise disruptions. Additionally, ensure your mattress and pillows provide adequate support and comfort for a restful sleep.
Impact of Noise and Light on Sleep Quality
Noise and light can significantly impact the quality of your sleep. Exposure to excessive noise can disrupt sleep patterns and prevent you from entering deep, restorative sleep stages. Likewise, exposure to bright light, especially blue light emitted by electronic devices, can interfere with your body’s natural sleep-wake cycle. Minimizing noise and light disturbances in your sleep environment can help ensure a more restful and restorative sleep.
Effects of Temperature and Humidity on Sleep
Temperature and humidity levels in your sleep environment can also affect sleep quality. Your body temperature naturally decreases during sleep, so it’s important to keep your bedroom cool to facilitate this process. Ideally, aim for a room temperature between 60-67°F (15-19°C). Additionally, excessive humidity can lead to discomfort and disrupt sleep. Using a dehumidifier or adjusting your bedroom’s ventilation can help maintain optimal sleep conditions.
Monitoring Sleep and Recovery
Using Wearable Technology for Sleep Tracking
Wearable technology, such as fitness trackers and smartwatches, can be valuable tools for monitoring sleep and recovery. These devices use sensors to track your sleep patterns, including duration, time spent in different sleep stages, and quality of sleep. By analyzing this data, you can gain insights into your sleep habits and make necessary adjustments to optimize your recovery and performance.
Sleep Metrics and their Interpretation
Sleep trackers provide various metrics that can help you understand your sleep patterns. These metrics may include total sleep time, sleep efficiency, time spent in each sleep stage, and the number of awakenings during the night. Understanding these metrics can allow you to identify any issues or patterns affecting your sleep quality and make informed decisions to improve your recovery and performance.
Tracking Recovery Indicators during Sleep
Sleep plays a crucial role in the recovery process, and monitoring recovery indicators during sleep can provide valuable insights. Some wearable devices offer features that track heart rate variability (HRV) and body temperature, which can indicate your body’s level of recovery. By tracking these indicators, you can adjust your training load and recovery strategies to ensure optimal performance and minimize the risk of overtraining.
Strategies for Improving Sleep Quality
Establishing a Consistent Sleep Schedule
Establishing a consistent sleep schedule is a fundamental strategy for improving sleep quality. Aim to go to bed and wake up at the same time each day, even on weekends. This consistency helps regulate your body’s internal clock, promoting better sleep quality and overall well-being. Avoiding napping close to bedtime and limiting exposure to stimulating activities, such as electronics and intense exercise, before bed can also contribute to better sleep.
Creating a Relaxing Bedtime Routine
Creating a relaxing bedtime routine can signal to your body that it’s time to wind down and prepare for sleep. Engage in calming activities, such as reading a book, taking a warm bath, or practicing relaxation techniques like deep breathing or meditation. Avoid engaging in stimulating or stressful activities that can interfere with your ability to relax and fall asleep.
Optimizing Nutrition and Hydration for Sleep
Nutrition and hydration play a significant role in sleep quality. Avoid consuming large meals or heavy, spicy, or greasy foods close to bedtime, as they can cause discomfort and disrupt sleep. Instead, opt for light, easily digestible snacks that contain sleep-promoting nutrients, such as complex carbohydrates, lean proteins, and magnesium-rich foods. Staying hydrated throughout the day, while also limiting excessive fluid intake before bed, can contribute to better sleep quality.
Nutrition and Sleep
Foods that Promote Sleep
Certain foods contain nutrients that can promote better sleep. For example, foods rich in tryptophan, such as turkey, dairy products, and nuts, can help increase the production of serotonin, a precursor to melatonin, the sleep hormone. Other sleep-promoting foods include whole grains, bananas, cherries, and herbal teas like chamomile. Incorporating these foods into your diet, especially in the evening, can support better sleep quality.
Timing of Meals and its Impact on Sleep
The timing of your meals can also impact your sleep quality. It’s generally recommended to avoid heavy meals or large amounts of food close to bedtime, as digestion can disrupt sleep. Aim to have your last meal or snack at least 2-3 hours before bed to allow for proper digestion. If you feel hungry before bedtime, opt for a light, sleep-promoting snack to satisfy cravings without causing digestive discomfort.
Effects of Caffeine and Alcohol on Sleep
Caffeine and alcohol can significantly affect your sleep. Caffeine is a stimulant that can interfere with falling asleep and disrupt the overall quality of your sleep. It is advisable to avoid consuming caffeinated beverages or foods close to bedtime. Similarly, while alcohol may initially make you feel drowsy, it can disrupt the natural sleep cycle, leading to fragmented and less restful sleep. It’s best to limit or avoid alcohol consumption, especially in the evening, to optimize your sleep quality.
Sleep Disorders and Athletes
Common Sleep Disorders among Athletes
Athletes are not immune to sleep disorders. Common sleep disorders that can affect athletes include insomnia, sleep apnea, restless leg syndrome, and circadian rhythm disorders. These disorders can significantly impact sleep quality, exacerbate daytime fatigue, and hinder athletic performance. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of sleep disorders is important so that appropriate interventions can be sought.
Impact of Sleep Disorders on Performance
Sleep disorders can have a profound negative impact on an athlete’s performance. Insufficient sleep, fragmented sleep, or poor sleep quality can impair cognitive function, decision-making, motor skills, and reaction time. Athletes with sleep disorders may experience decreased endurance, slower recovery, increased injury risk, and difficulties with mental focus and concentration. Addressing sleep disorders is crucial for optimizing athletic performance and overall well-being.
Seeking Professional Help for Sleep Issues
If you suspect you have a sleep disorder or are experiencing persistent sleep issues, it is essential to seek professional help. Consulting a healthcare professional, such as a sleep specialist or sports medicine physician, can help diagnose and treat any underlying sleep disorders. They can provide personalized recommendations, interventions, and treatment options tailored to your specific needs, ensuring you receive the necessary support to optimize your sleep and athletic performance.
Napping as a Recovery Strategy
Benefits of Power Naps for Athletes
Napping can be an effective strategy to enhance recovery in athletes. Power naps, short naps lasting around 10-20 minutes, can help alleviate fatigue, promote alertness, and enhance cognitive function. These quick naps can provide a boost of energy and help you feel refreshed during training or competition, especially when facing sleep deficits or long periods of wakefulness.
Optimal Duration and Timing of Naps
The optimal duration and timing of naps may vary depending on individual preferences and sleep needs. Generally, power naps lasting around 10-20 minutes are recommended, as they can provide restorative benefits without causing grogginess upon waking. It is important to avoid napping too close to bedtime or for extended periods, as this can interfere with your nighttime sleep. Experiment with different nap durations and timings to discover what works best for you.
Incorporating Naps into Training Schedules
Incorporating naps into your training schedule can enhance your overall recovery and performance. If your training schedule allows, consider scheduling a power nap during the day, especially after intense workouts or periods of high mental exertion. Finding a quiet, comfortable space to rest and recharge can contribute to faster recovery, increased alertness, and improved productivity throughout the day.
Sleep and Injury Risk
The Relationship Between Sleep and Injury
There is a clear relationship between sleep and injury risk among athletes. Inadequate sleep can impair coordination, reaction time, and decision-making abilities, increasing the likelihood of accidents and injuries during training or competition. Additionally, insufficient sleep can compromise your immune function, making you more susceptible to illnesses and infections, which can also hinder your athletic performance and recovery.
Reducing the Risk of Injuries through Quality Sleep
Prioritizing quality sleep can help reduce the risk of injuries in athletes. By ensuring you obtain adequate sleep, you enhance your cognitive function, coordination, and reaction time, reducing the likelihood of accidents and mistakes. Furthermore, sufficient sleep supports optimal immune function, improving your body’s ability to fight off infections and speed up injury recovery. By taking care of your sleep, you invest in your overall health and injury prevention.
Importance of Sleep in Injury Rehabilitation
Sleep plays a critical role during injury rehabilitation. It is during sleep that your body repairs damaged tissues, replenishes energy stores, and optimizes the healing process. Adequate sleep supports the recovery and rehabilitation process, allowing your body to heal faster and more efficiently. If you’re recovering from an injury, prioritize quality sleep alongside your rehabilitation efforts to maximize your recovery potential and promote optimal healing.
In conclusion, sleep is a vital component of an athlete’s overall performance and well-being. Adequate sleep supports physical and cognitive recovery, enhances athletic performance, and reduces the risk of injuries. By understanding the different sleep stages, monitoring sleep quality, and implementing strategies to optimize sleep duration and environment, athletes can maximize their potential both on and off the field. Prioritizing sleep and seeking professional help when needed can make a significant difference in an athlete’s overall health, performance, and longevity in their athletic journey. So, make sleep a priority and reap the benefits of quality rest.